What is Gall Bladder?
The gallbladder is located in the right upper abdomen beneath the liver and store digestive juice produced by the liver (Bile). After eating bile is released from Gall Bladder into small intestine that helps the body to digest fat.
What is Cholecystitis ?
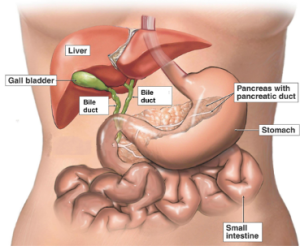
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder wall and nearby abdominal lining. Acute cholecystitis is the sudden onset of inflammation of the gallbladder, resulting in severe, steady upper abdominal pain (biliary colic), which may occur repeatedly. Chronic Cholecystitis is long-standing inflammation of the gallbladder characterized by repeated attacks of pain (gallbladder attacks) over a prolonged period.
At least 95% of people with acute cholecystitis have gallstones.
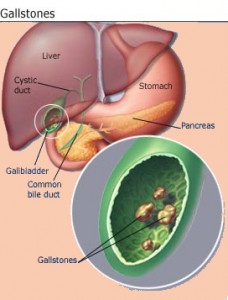
What is Gall Stones?
A gall stone is a lump of hard material formed inside the gall bladder. These stones may block the flow of bile out of the gall bladder causing it to swell.It is uncertain why some people form gall stones but certain people are more at risk than others.
Risk Factor for Gall Stones/People at Risk of Gall Bladder Stones
- Females
- overweight or obesity
- Pregnancy
- High-fat & High Cholesterol, Low fiber l Diet
- Family history of gallstones
- Diabetes
- Losing weight too quickly
- Medication: some cholesterol-lowering medications, hormone therapy containing estrogen
What are the Symptoms of Gall Bladder Stones?
Many people with gallstones have no symptoms (silent stones).
Symptoms usually follow after fatty meals:
Symptoms usually follow after fatty meals:
- Abdominal bloating
- Intolerance of fatty food
- Abdominal Pain
- Nausea, vomiting
- Indigestion, belching
- Occasionally fever
- Jaundice if Gall stone blocks common bile duct
How to Diagnose Gallstones?
Thorough history and abdominal examination may give clues. Ultrasonography of abdomen is most sensitive and specific test to diagnose. Certain blood tests are advised for signs of infection, jaundice, or pancreatitis Sometimes CT scan HIDA scan or ERCP (endoscopic retrocholangio pancreatography) may be required.
What is Treatment of Gall Bladder Stones?
Why to remove Gall Bladder, Why not remove only Gall Stones?
If Gall Bladder stone is not causing any symptom it can be kept on watchful waiting with low fat high fiber diet (Beans , bran, cereals ), more fruits and vegetables and regular exercise.
For Symptomatic stones medicines such as antibiotics and pain killers are given for short term relief.
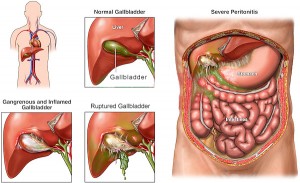
Permanent cure to problem is removal of the gall bladder & not the stones only as Gall stone may form again. Not removing gall bladder may worsen infection with bursting of Gall Bladder.
By removing infected gall bladder we are safeguarding against a lot of complications like Cholecystitis & Pancreatitis.Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Open surgery requires a long cut through skin and muscles to expose the area to be operated. Laparoscopic or key hole surgery is less invasive. Read more about laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Effect Of Gall Bladder Removal on Digestion
To conclude we can say the treatment of gall stones is the removal of the gall bladder not the stones only and there is no ill effect of Gall bladder removal on normal digestion. Contrary to common belief you can eat fatty meal even after Gall Bladder surgery. Fat is digested with the help of bile which is secreted from liver. Gall Bladder merely stores it.Doing timely gall bladder surgery we may safeguard against a lot of Complications like Cholecystitis & Pancreatitis. Laparoscopic gall bladder surgery is gold standard.
Our Specialist

Dr. Nitish Jhawar
M.S., FMAS, FIAGES, FALS, FACRSI
Fellow Advance Laparoscopic Surgery
Fellow Colorectal Surgery USA
Senior Laparoscopic & Colorectal Surgeon
Phone No: +91 9322 229 159
Email Id: info@neoalta.com

