What is Hernia?
Most hernias are detected by a surgeon during a physical examination
Causes & Contributing Risk Factors for Hernia
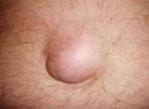
What are the Symptoms of Hernia?
- The most common symptom of a hernia is a painless lump in the groin or in males a bulge in the scrotum.
- This may present with straining while lifting heavy objects, during a bowel movement, coughing or sneezing.
- The lump may disappear on lying down or even with gentle pressure. A small hernia may not even be noticed and may only be detected during a routine examination.
- Severe continuous pain, redness, and tenderness are signs that a hernia may be entrapped or strangulated.
- A hernia is dangerous if it gets trapped in the weak spot in the abdominal wall (obstructed Hernia) and blood supply cut off (strangulated Hernia). Strangulated hernia is an emergency requiring surgery.
How to Diagnose Hernia?
A hernia is usually diagnosed by a surgeon through a simple physical examination. He can feel a hernia by placing a finger in the groin and asking the patient to a cough (impulse on coughing).
A hernia that bulges out with abdominal pressure but returns inside the body when the pressure is gone or with gentle pressure from the outside is a reducible hernia.
A Hernia that remains outside is “irreducible” or incarcerated hernia.
If bulging tissue loses blood flow it is the strangulated hernia.
Functional classification of Hernia:
Grade I
-
Swelling appears on coughing/straining and disappears on lying down
-
Defect size finger breadth
Grade II
-
Small, indirect, incomplete reducible hernia
-
Swelling limited to inguinal canal
-
Moderate size direct hernia
-
Swelling present on standing and reduces in the supine position
-
Defect thumb size
-
Small indirect reducible
-
Reducible femoral hernia
Grade III
-
Moderate size indirect reducible
-
Swelling extends up to neck of the scrotum but not to the testis
-
Large reducible direct hernia
-
Recurrent groin hernia
Grade IV
-
Large, reducible, indirect
-
Sac extending up to testis
Grade V
- Large complete indirect inguinal hernia partially reducible or irreducible
- Irreducible femoral hernia
Types of Hernia:
Inguinal (Groin)
Femoral Hernias
Umbilical Hernias
Ventral Hernias
Epigastric Hernias
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH)
Stomach or other organs of abdomen may enter into the chest. Hiatal hernias may be incidental finding in chest X-Ray or may present as heartburn, regurgitation, reflux, chest pain, difficulty swallowing or painful swallowing.
Hiatal hernias can be treated with medication and diets changes, but sometimes require surgery.
Incisional Hernia: Occurs at the site of a prior abdominal incision. Parastomal Hernia: Occurs at the site of a colostomy, ileostomy or other stoma (intestines sutured to the skin).
Spigelian Hernia: Occurs in the lower quadrants of the abdomen, usually at or below the level of the belly button.
Treatment of Hernia- Medicine or Surgery?
Prevention of Hernia?
- Maintain healthy weight: healthy weight is determined by your height measured by BMI (Body mass Index) Overweight causes stress on body. Consult your dietician for diet and exercise plan.
- Coughing should be shown to doctor. Quit smoking
- Allergy causing excess sneezing and coughing should be treated
- Eat fruits, vegetables and grains to avoid constipation
- Do not lift weight more than you can handle
Our Specialist

Dr. Nitish Jhawar
M.S., FMAS, FIAGES, FALS, FACRSI
Fellow Advance Laparoscopic Surgery
Fellow Colorectal Surgery USA
Senior Laparoscopic & Colorectal Surgeon
Phone No: +91 9322 229 159
Email Id: info@neoalta.com

